Built-in Functions |

|

|

|
||
Built-in Functions |

|

|

|

|
|
|
||
Overview of the Built-in Functions
There are many built-in functions available to help you define your formulas. The most commonly used of these functions are as follows:
To take the average of values: AVERAGE(X1, X2,...)
To take the summation of values: SUM(X1, X2,...)
To take the minimum of values: MIN(X1, X2,...)
To take the maximum of values: MAX(X1, X2,...)
To take the product of values: PROD(X1, X2,...)
When you call a function, you must supply an actual values for all function's arguments, and separate them with a comma (','). Formula functions are not case sensitive and therefore the formula functions can be entered in both uppercase and lowercase letters.
Functions can also contain constants unless otherwise specified. For more information on constant types, see Constants.
When function parameters are derived from other functions or expressions, it is possible that parameters will not get values at all. Since regular functions cannot handle these so-called NIL values, the calculation will end to an error. In order to ignore NIL values in your formula calculations, you can enter the underscore character "_" after the function name. Therefore AVERAGE_(X1, X2,...), SUM_(X1, X2,...), MIN_(X1, X2,...), etc., are all valid functions with the exception of ignoring all supplied NIL values.
Functions that return lists of values (such as CUMULATIVE and RANGE) should not be used in formulas directly but in combination with aggregate functions such as SUM, AVERAGE, MAX, or MIN.
For example, the formula AVERAGE_(NIL,2,NIL,3), where NIL represents an undefined (null) value, will be calculated as AVERAGE(2,3).
Function Categories
•Conversion and Rounding Functions
•Math and Trigonometry Functions
In addition, there are different operators and wildcards available:
Consolidation Functions
Returns list of values, accumulated to the period level of the element in which the function is. |
|
Returns a list of cumulative values, one per each expression. |
|
Returns the sum of the arguments. |
ACCUMULATE
Description
Returns list of values, accumulated to the period level of the element in which the function is.
Syntax
ACCUMULATE(expression_list, accumulation_rule)
Parameters: expression_list, accumulation_rule
expression_list contains an even number of expressions separated by commas. The list has references to value series first and then either a date series or NIL reference for each value series.
accumulation_rule is one of the following values enclosed in double quotes: DEFAULT, SUM, SUM_, AVERAGE, AVERAGE_, MIN, MAX, FIRST, LAST, or LATEST.
Examples
ACCUMULATE(mea1.act(), NIL, "default") : Accumulate mea1.act() using accumulation rule of mea1 (same as "mea1.act()")
ACCUMULATE(mea1.act(), NIL, "sum_") : Accumulate mea1.act() using accumulation rule sum_ (override element's own accumulation rule with sum_)
ACCUMULATE(mea1.act(), mea1.date(), "average_") : Accumulate mea1.act() using accumulation rule average_. Accumulated values are selected (targeted to periods)
according to dates found in mea1.date().
ACCUMULATE(mea1.act(), mea2.act(), NIL, mea3.dates(), "default") : accumulate values from mea1.act() and mea2.act() with the element's own accumulation rule.
Select accumulated values for mea2.act() on the basis of the dates found in mea3.dates() series.
CUMULATIVE
Description
Returns a list of cumulative values, one per each expression. In the case there are null values in the results, they must be controlled with container functions such as SUM_ or AVERAGE_ (for example, SUM_(CUMULATIVE(?.act(), 1, SUM_)) or the CUMULATIVE_ function must be used.
Syntax
CUMULATIVE(expression_list,relative level,formula )
CUMULATIVE_(expression_list,relative level,formula )
Parameter: expression_list
A list of expressions separated by commas. An expression is a reference to element's series on a certain period.
Parameter: relative level
An integer value stating which period level will be used in the calculation. The number is a relative value, pointing upward in the period level hierarchy. Values less than 1 are considered invalid.
Parameter: formula
This parameter determines which function will be used for calculating the cumulative values. The following function names are valid: SUM, SUM_, AVERAGE, and AVERAGE_.
Examples
This function returns the average of all mea1 measure values. The calculation will start at the beginning of a period which is one level higher than the period level of sc1.mea1.
CUMULATIVE(sc1.mea1.act(),1,AVERAGE)
This function returns a cumulative sum for actual and alarm series of the current measure, scorecard and period. The calculation will start at the beginning of a period which is two levels higher than the period level of sc1.mea1.
CUMULATIVE(sc1.mea1.act(),sc1.mea1.alarm(),2,SUM)
This function calculates a cumulative sum of sales. Calculation is done with all scorecards' sales elements, closed series. Sum is cumulated one period level upwards from the sales-element's own period level. For instance, if sales is measured in day level and 'month' is next period level upwards from 'day', then cumulative sum is calculated for monthly level.
SUM_(CUMULATIVE(?.SALES.CLOSED(), 1, SUM_))
See also
SUM
Description
Returns the sum of the arguments.
Syntax
SUM(X1, X2, ... )
SUM_(X1, X2, ... )
Parameter: X
Any numeric expression.
Examples
This function returns 16.
SUM(1,12,3)
Conversion and Rounding Functions
Rounds a number up to the nearest integer value. |
|
Recalculates the series that is given as a parameter. |
|
Rounds a number down to the nearest integer value. |
|
Returns a list of range values, one per each expression. |
|
Rounds the given number to an integer value. |
|
Returns an integer value depending on the parameters sign. |
|
Truncates decimal number to integer number. |
CEIL
Description
Rounds a number up to the nearest integer value.
Syntax
CEIL(number )
Parameter: number
The value to round.
Remarks
Both negative and positive values are always rounded up, i.e. negative values go to the next integer value towards zero, positive values go to the next integer value away from zero. Measure identifiers can be used instead of numbers.
Examples
This function returns 2:
CEIL(1.23459)
This function returns 149:
CEIL(148.24)
This function returns -1:
CEIL(-1.5)
See also
AVERAGE, FLOOR, MAX, MIN, ROUND.
FETCH
Description
Recalculates the value of the given series by using the period for which the calculation is done, instead of using the value of the matching period in the period level of the series given. If the input type of the series is not formula, returns the values of the parameter series.
Syntax
FETCH(identifier )
Parameter: identifier
The identifier of the series for which the value is to be recalculated.
See also
FLOOR
Description
Rounds a number down to the nearest integer value.
Syntax
FLOOR(number )
Parameter: number (or measure identifier )
The value to round.
Remarks
Both negative and positive values are rounded down.
Examples
This function returns 1:
FLOOR(1.23459)
This function returns -149:
FLOOR(-148.24)
See also
AVERAGE, CEIL, MAX, MIN, ROUND.
RANGE
Description
Returns a list of range values, one per each expression. In the case there are null values in the results, they must be controlled with container functions such as SUM_ or AVERAGE_ (for example, SUM_(RANGE(?.ACT())).
Note: You can use also the abbreviated form R as this function's name.
Ignore null version of this function is not supported. Both ignore null values and normal versions of this function work similarly.
Syntax
RANGE(EXPRESSION1, EXPRESSION2, ... )
RANGE_(EXPRESSION1, EXPRESSION2, ... )
Parameter: EXPRESSION
Any valid expression.
Examples
This function returns the range value of mea1:
RANGE(mea1.act1(latest))
This function returns all range values of the latest period of all existing measures, where measure identifier is mea1 and series identifier is act1. Values will be separated by comma.
RANGE(?.mea1.act1(latest))
ROUND
Description
Rounds the given number to an integer value. Negative values are rounded symmetrically, i.e. -0.5 is rounded to -1.
Syntax
ROUND(number,amount of decimals)
Parameters:
Number, any value or measure identifier.
Amount of decimals, the precision to which the number is rounded, i.e. the number of decimals present in the result. Giving 0 rounds to the nearest even number. Note that the amount of decimals can also be negative.
Examples
This function returns 12.4:
ROUND(12.44, 1)
This function returns 12:
ROUND(12.44,0)
This function returns 10:
ROUND(12.44,-1)
This function returns 100:
ROUND(113,-2)
See also
AVERAGE, CEIL, FLOOR, MAX, MIN.
SIGN
Description
Returns an integer value depending on the parameters sign.
Syntax
SIGN(number )
Sign of X; =1 for X>0, =0 for X=0, =-1 for X<0
Examples
This function returns 1 :
SIGN(5)
This function returns 0 :
SIGN(0)
This function returns -1 :
SIGN(-5)
TRUNC
Alias
INT
Description
Truncates decimal number to integer number.
Syntax
TRUNC(number )
Parameter: number
A real number.
Examples
This function returns 1.
TRUNC(1.5134)
This function returns -13.
TRUNC(-13.15)
See also
Date and Time Functions
Returns the current date. |
|
Returns a number representing a datetime given as the parameter. |
|
Returns the number of the day, of date. This is the number of days passed in the month. |
|
Returns a TDateTime type for a specified Year, Month, and Day. |
|
Returns the number of hours in a datetime. |
|
Returns the number of minutes (0-59) in a datetime. |
|
Returns the month date is in. January is one. |
|
Returns period's last date |
|
Returns period's first date. |
|
Returns the number of seconds (0-59) in a datetime. |
|
Returns a number representing the Hour, Minute, and Second given as parameters. |
|
Returns the day of the week of the specified date as an integer between 1 and 7. |
|
Returns the year date is in. |
DATE
Description
The Date function returns the current date.
Syntax
DATE()
DATETIME
Description
The DateTime function returns a number representing a datetime given as the parameter. The value is a number representing time that has passed since 12/30/1899. The Year must be between 1 and 9999. Valid Month values are 1 through 12. Valid Day values are 1 through 28, 29, 30, or 31, depending on the Month value. For example, the possible Day values for month 2 (February) are 1 through 28 or 1 through 29, depending on whether or not the Year value specifies a leap year. Valid Hour values are 0 through 23. Valid Minute values are 0 through 59. Valid Second values are 0 through 59.
Syntax
DATETIME(Y,M,D,H,M,S)
DAY
Description
Returns the number of the day, of date. This is the number of days passed in the month.
Syntax
DAY(D)
The date specified in D.
DAYOFWEEK
Description
The DAYOFWEEK function returns the day of the week of the specified date as an integer between 1 and 7. Sunday is the first day of the week and Saturday is the seventh. Note that this function is included for backward compatibility only. Please use WEEKDAY instead.
Syntax
DAYOFWEEK(D)
The date specified in D.
ENCODEDATE
Description
EncodeDate returns a TDateTime type for a specified Year, Month, and Day. The TDateTime value is the number of days that have passed since 12/30/1899.
The Year must be between 1 and 9999. Valid Month values are 1 through 12. Valid Day values are 1 through 28, 29, 30, or 31, depending on the Month value. For example, the possible Day values for month 2 (February) are 1 through 28 or 1 through 29, depending on whether or not the Year value specifies a leap year.
Syntax
ENCODEDATE(Y,M,D)
The year is specified in Y, the month is specified in M and the date specified in D.
Example
This function returns 37,378.00 :
ENCODEDATE(2002,5,2)
EXTRACTDAY
Description
Returns the number of the day, of date. This is the number of days passed in the month. Note that this function is included for backward compatibility only. Please use DAY instead.
Syntax
EXTRACTDAY(D)
The date specified in D.
EXTRACTMONTH
Description
Returns the month date is in. January is one. Note that this function is included for backward compatibility only. Please use MONTH instead.
Syntax
EXTRACTMONTH(D)
The date specified in D.
EXTRACTYEAR
Description
Returns the year date is in. Note that this function is included for backward compatibility only. Please use YEAR instead.
Syntax
EXTRACTYEAR(D)
The date specified in D.
HOUR
Description
Returns the number of hours in a datetime.
Syntax
HOUR(D)
The datetime specified in D.
MINUTE
Description
Returns the number of minutes (0-59) in a datetime.
Syntax
MINUTE(D)
The datetime specified in D.
MONTH
Description
Returns the month date is in. January is one.
Syntax
MONTH(D)
The date specified in D.
PERIODEND
Description
Returns period's last date.
Syntax
PERIODEND()
PERIODSTART
Description
Returns period's first date.
Syntax
PERIODSTART()
SECOND
Description
Returns the number of seconds (0-59) in a datetime.
Syntax
Second(D)
The datetime specified in D.
TIME
Description
Returns a number representing the Hour, Minute, and Second given as parameters. Hour values are 0 through 23. Minute and Second values are 0 through 59
Syntax
TIME(H,M,S)
The time specified in H, M, and S.
WEEKDAY
Description
The WEEKDAY function returns the day of the week of the specified date as an integer between 1 and 7. Sunday is the first day of the week and Saturday is the seventh.
Syntax
WEEKDAY(D)
The date specified in D.
YEAR
Description
Returns the year date is in.
Syntax
YEAR(D)
The date specified in D.
Logical Functions
Tests the condition and returns the specified value. |
|
Tests if the value of the parameter given to it is NULL. |
|
Takes an element value or built-in formula function as an input. If the result is NIL (there is no value) the return value is given. Otherwise the input value is returned. |
IIF
Description
Tests the condition and returns the specified value.
Syntax
IIF(condition , true_value, false_value )
Parameter: condition
Any logical expression. As evaluation order may affect the results, it is recommended to use parentheses with longer expressions, for example IIF(MEA1.ACT()+1=2, true, false) should be input as IIF((MEA1.ACT()+1)=2, true, false)
Parameter: true_value
The value to be returned if condition evaluates to True (i.e. <>0).
Parameter: false_value
The value to be returned if condition evaluates to False (i.e. =0).
Examples
This function returns 5 if the "Actual" value (series identifier "ACT") of MEA1 is greater than 10 and 2 if the "Actual" value of MEA1 is less than 10:
IIF(MEA1.ACT()>10, 5, 2)
ISNULL
Description
Tests if the value of the parameter given to it is NULL and returns 0 if the value is not NULL or 1 if it is NULL. If the parameter contains several measure values or it is a number list, the function returns a number list indicating the NULL value of each measure value or number in the list. Number lists are tested in listed order, but the testing order of measure values is not defined. Note: Using a function that ignores NULL values as the parameter for ISNULL is not supported. For example, functions like ISNULL(SUM_(NULL,1)) will return 1, even though it would seem they shouldn't.
Syntax
ISNULL(X)
Parameter: X can be any number, number list or measure identifier.
Examples
When ?.ACT contains three measures with no NULL values:
This function returns [0 0 0]:
ISNULL(?.ACT)
When ?.ACT contains three measures with one having a NULL value:
This function returns [0 1 0]
ISNULL(?.ACT)
COALESCE
Description
The Coalesce function takes an element value or built-in formula function as an input. If the result is NIL (there is no value) the return value is given. Otherwise the input value is returned.
Syntax
COALESCE(Input Value, Return Value )
Input value can be either element's value for certain series or one of QPR Metrics's built-in functions.
Return value can be a number, element's value for a certain series or one of QPR Metrics's built-in functions.
Examples
In the following examples, the current period is period2 and Actual ("ACT") and Simulation ("SIM") are series of the elements. The elements MEA1 and MEA2 have the following values:
For MEA1: |
For MEA2: |
Period 1, Actual value = 1 Period 2, Actual value = N/A |
Period 1, Actual value = 2 Period 1, Simulation value = N/A Period 2, Actual value = 2 Period 2, Simulation value = 3 |
This function, with Input value MEA1.ACT() and Return value 0, returns the value 0 because the input value is not available:
Coalesce(MEA1.ACT(), 0)
= Coalesce(N/A,0)
This function, with Input value SUM(MEA1.ACT(-1), MEA2.SIM()) and Return value MEA2.ACT(-1), returns the value 4 :
Coalesce(SUM(MEA1.ACT(-1), MEA2.SIM()), MEA2.ACT(-1))
= Coalesce(SUM(1,3),2)
= Coalesce(4,2)
Math and Trigonometry Functions
Returns the absolute value of the number. |
|
Returns the arc cosine. |
|
Returns argument (phase) of X and Y. |
|
Returns the arc sine. |
|
Returns the arc tangent. |
|
Returns the cosine of an angle. |
|
Returns the hyperbolic cosine. |
|
Returns the cotangent. |
|
Returns e raised to a power number , where e is the base of the natural logarithms. |
|
Returns the fractional part of an argument. |
|
Returns X raised to a power of Y. |
|
Returns the log base 10 for X. |
|
Returns the natural log of a real expression X. |
|
Returns the log base 2 for X. |
|
Raises Base to the power specified by Exponent. |
|
Returns the product of arguments. |
|
Returns the length of a circle's radius |
|
Returns the sine of an angle. |
|
Returns the hyperbolic sine. |
|
Returns the square of a number. |
|
Returns the square root of a number. |
|
Returns the tangent of an angle. |
|
Returns the hyperbolic tangent. |
|
Returns 0 if the given argument is 0. Otherwise the function returns 1. |
ABS
Description
Returns the absolute value of the number.
Syntax
ABS(number )
Parameter: number
the number argument can be any valid numeric expression.
Examples
These functions return 8 :
ABS(-8) and ABS(8)
See also
ACOS
Description
Returns the arc cosine. Since arc cosine is the inverse function of cosine, it returns an angular radian value.
Syntax
ACOS(X)
Parameter: X, where -1 <= X <= 1
Examples
This function returns 1.0471975511965976 :
ACOS(0.5)
See also
ASIN, ATAN, COS, COSH, COTAN, SIN, SINH, TAN, TANH.
ARG
Description
Returns argument (phase) of X and Y.
Syntax
ARG(X,Y)
Parameters: X and Y
the arguments X and Y can be a positive or negative decimal number.
Examples
This function returns 0.46 :
ARG(2,1)
This function returns 0 :
ARG(3,0)
See also
ASIN
Description
Returns the arc sine. Since arc sine is the inverse function of sine, it returns an angular value.
Syntax
ASIN(X)
Parameter: X, where -1 <= X <= 1
Examples
This function returns 1.5707963267948966 :
ASIN(1)
See also
ACOS, ATAN, COS, COSH, COTAN, SIN, SINH, TAN, TANH.
ATAN
Description
Returns the arc tangent. Since arc tangent is the inverse function of tangent, it returns an angular radian value.
Syntax
ATAN(X)
Parameter: X, where X can be any number.
Examples
This function returns 0.7853981633974483 :
ATAN(1)
See also
ASIN, ACOS, COS, COSH, COTAN, SIN, SINH, TAN, TANH.
COS
Description
Returns the cosine of an angle.
Syntax
COS(angle )
Parameter: angle
Angle is any valid numeric expression, measured in radians.
Examples
This function returns -0.9899924966004454 :
COS(3)
See also
ASIN, ACOS, ATAN, COSH, COTAN, SIN, SINH, TAN, TANH.
COSH
Description
Returns the hyperbolic cosine.
Syntax
COSH(angle )
Parameter: angle
Angle is any valid numeric expression, measured in radians.
Examples
This function returns 10.067661995777765 :
COSH(3)
See also
ASIN, ACOS, ATAN, COS, COTAN, SIN, SINH, TAN, TANH.
COTAN
Description
Returns the cotangent.
Syntax
COTAN(angle )
Parameter: angle
Angle is any valid numeric expression, measured in radians.
Examples
This function returns 1.461696 :
COTAN(0.6)
See also
ASIN, ACOS, ATAN, COS, COSH, SIN, SINH, TAN, TANH.
EXP
Description
Returns e raised to a power number , where e is the base of the natural logarithms.
Syntax
EXP(number ) = ![]()
Parameter: number
the number argument can be any valid numeric expression.
Examples
This function returns 1.
EXP(0)
This function returns 2.718282 :
EXP(1)
See also
FRAC
Description
Returns the fractional part of an argument.
Syntax
FRAC(number )
Parameter: the number argument can be any valid numeric expression.
Examples
This function returns 0.1415 :
FRAC 3.1415
IPOWER
Description
Returns X raised to a power of Y. This function converts the arguments into integer values (by ignoring the decimal part) before executing the calculation.
Syntax
IPOWER(X,Y)
Parameters: X can be any valid numeric expression. Y is an integer value.
Examples
This function returns 8:
IPOWER(2,3)
This function returns 27 (the decimal part is ignored):
IPOWER(3.2,3)
LG
Description
The LG function returns the log base 10 for X.
Syntax
LG(X)
Parameter: X > 0.
Examples
10^X = 1000, to find out the X use LG function.
X= lg(1000) = 3
6^X = 1296, to find out the X use LG function
X= lg(1296)/lg(6) = 4
See also
LN
Description
LN returns the natural log of a real expression X.
Syntax
LN(X)
Parameter: X > 0.
Examples
This function returns 0.693147 :
LN(2)
This function returns 2.302585 :
LN(10)
See also
LOG
Description
The LOG function returns the log base 2 for X.
Syntax
LOG(X)
Parameter: X > 0.
Examples
2^X= 256, to find out the X, use LOG function.
X = LOG(256) = 8
See also
POWER
Description
Power raises Base to the power specified by Exponent.
Syntax
POWER(X,Y)
Parameter:
X, base can be any valid numeric expression.
Y, exponent is a floating point value.
Examples
This function returns 4 :
POWER(16,0.5)
PROD
Description
Product of arguments.
Syntax
PROD(X1,X2,...)
PROD_(X1,X2,...)
Parameter:X ,
Any valid numeric expression.
RADIUS
Description
Returns the length of a circle's radius, where the radius is the hypotenuse of the right-angled triangle with vertices at (0,0), (X,Y), and (X,0).
Syntax
RADIUS(X,Y) = sqrt(sqr(X)+sqr(Y))
See also
SIN
Description
Returns the sine of an angle.
Syntax
SIN(angle )
Parameter: angle
Angle is any valid numeric expression, measured in radians.
Examples
This function returns 0.1411200080598672.
SIN(3)
See also
ASIN, ACOS, ATAN, COS, COSH, COTAN, SINH, TAN, TANH.
SINH
Description
Returns the hyperbolic sine.
Syntax
SINH(angle )
Parameter: angle
Angle is any valid numeric expression, measured in radians.
Examples
This function returns 10.017874927409903.
SINH(3)
See also
ASIN, ACOS, ATAN, COS, COSH, COTAN, SIN, TAN, TANH.
SQR
Description
Returns the square of a number.
Syntax
SQR(number )
Parameter: number
Any valid numeric expression greater than or equal to 0.
Examples
This function returns 9.
SQR(3)
SQRT
Description
Returns the square root of a number.
Syntax
SQRT(number )
Parameter: number
A non-negative integer or a decimal number.
Examples
This function returns 16.
SQRT(256)
TAN
Description
Returns the tangent of an angle.
Syntax
TAN(angle )
Parameter: angle
Any valid numeric expression, measured in radians.
Examples
This function returns -0.1425465430742778.
TAN(3)
See also
ASIN, ACOS, ATAN, COS, COSH, COTAN, SIN, TANH.
TANH
Description
Returns the hyperbolic tangent.
Syntax
TANH(angle )
Parameter: angle
Any valid numeric expression, measured in radians.
Examples
This function returns 0.9950547536867306.
TANH(3)
See also
ASIN, ACOS, ATAN, COS, COSH, COTAN, SIN, TAN.
ZERO
Description
Returns 0 if the given argument is 0. Otherwise the function returns 1.
Syntax
ZERO(number ), =0 for X=0, =1 for X<>0
Parameter: number
Can be any valid numeric expression.
Examples
This function returns 0:
ZERO(0)
This function returns 1:
ZERO(135)
Statistical Functions
Returns the average of the supplied numbers. The result of AVERAGE is also known as the arithmetic mean. |
|
Returns the length of the given number list, object vector or string list. |
|
Returns the moving average based on the number of periods given with the delay given. |
|
Returns the largest value in the specified list of numbers. |
|
Returns the median in the specified list of numbers. |
|
Returns the smallest value in the specified list of numbers. |
|
Returns a random value between 0 and 1. |
|
Returns the standard deviation based on a sample. |
|
Returns the standard deviation based on the entire population given as arguments. |
|
Returns variance based on a sample. |
|
Returns variance based on the entire population. |
AVERAGE
Description
Returns the average of the supplied numbers. The result of AVERAGE is also known as the arithmetic mean. Numbers can be replaced by measure identifiers.
Syntax
AVERAGE(number_list )
AVERAGE_(number_list )
Parameter: number_list
A list of numbers or measure identifiers separated by commas. All numeric values (including 0) can be used.
Examples
This function returns 8.25:
AVERAGE(5, 6, 8, 14)
See also
COUNT
Description
Returns the length of the given number list, object vector or string list. If the parameter given to it is NULL, 0 is returned. If no parameters are given, 1 is returned.
Syntax
COUNT(list, x )
Parameters: list, x
List is any number list, object vector or string list.
X is either 0 or 1. Defines whether NULL values are included in the count or not. 0 = NULL values are not included (default), 1 = NULL values are included.
Examples
When ?.ACT has the following values: [0 NULL 1].
This function returns NULL:
COUNT(?.ACT)
This function returns 2:
COUNT_(?.ACT)
To calculate the total number of child measures having ACT-series (no matter if there are NULL values or not), the following function can be used:
COUNT_(?.ACT, 1)
MA
Description
Returns the moving average based on the number of periods given with the delay given.
Syntax
MA(dataseries, X, Y)
Parameters:
dataseries is the dataseries used for moving average calculation.
X is the number of periods used for the average calculation.
Y is the number of periods used as delay in the calculation
Examples
When MEA123.ACT() has the values [1,0 2,0 3,0 4,0 5,0 6,0 7,0 8,0 9,0 10,0]:
MA(MEA123.ACT(),3,0) returns [null null 2,0 3,0 4,0 5,0 6,0 7,0 8,0 9,0]
MA(MEA123.ACT(),3,2) returns [null null null null 2,0 3,0 4,0 5,0 6,0 7,0]
MAX
Description
Returns the largest value in the specified list of numbers.
Syntax
MAX(number_list )
MAX_(number_list )
Parameter: number_list, where number_list is a list of numbers separated by commas.
When the list contains one or more blank values, then the value returned is blank.
Examples
This function returns 500:
MAX(50, 100, 150, 500, 200)
See also
AVERAGE, CEIL, FLOOR, MIN, ROUND.
MEDIAN
Description
Returns the median in the specified list of numbers.
Syntax
MEDIAN(number_list)
MEDIAN_(number_list)
Parameter: number_list, where number_list is a list of numbers separated by commas.
The number_list can also be a dataseries.
Examples
When MEA123.ACT() has the values [1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10]:
MEDIAN(MEA123.ACT(AllToDate)) returns [1,0 1,5 2,0 2,5 3,0 3,5 4,0 4,5 5,0 5,5]
MEDIAN(MEA123.ACT(All)) returns [5,5 5,5 5,5 5,5 5,5 5,5 5,5 5,5 5,5 5,5]
MIN
Description
Returns the smallest value in the specified list of numbers.
Syntax
MIN(number_list )
_MIN(number_list )
Parameter: number_list, where number_list is a list of numbers separated by commas.
When the list contains one or more blank values, then the value returned is blank.
Examples
This function returns 50:
MIN(50, 100, 150, 500, 200)
See also
AVERAGE, CEIL, FLOOR, MAX, ROUND.
RANDOM
Description
Returns a random value between 0 and 1.
Syntax
RANDOM()
The Random function returns a random number within the range 0 <= X < 1.
STDEV
Description
Returns the standard deviation based on a sample. STDEV assumes that its arguments are a sample of the population. If your data represents the entire population, compute the standard deviation using STDEVP. The standard deviation is calculated using the "nonbiased" or "n-1" method using the following formula:
![]()
Syntax
STDEV(number_list)
STDEV_(number_list)
Parameter: number_list
A list of numbers or dataseries separated by commas.
Examples
When MEA123.ACT() has the values [1,0 2,0 3,0 4,0 5,0 6,0 7,0 8,0 9,0 10,0]:
STDEV(MEA123.ACT(AllToDate)) returns [null 0,7 1,0 1,3 1,6 1,9 2,2 2,4 2,7 3,0]
STDEV(MEA123.ACT(All)) returns [3,0 3,0 3,0 3,0 3,0 3,0 3,0 3,0 3,0 3,0]
See also
STDEVP
Description
Returns the standard deviation based on the entire population given as arguments. STDEVP assumes that its arguments are the entire population. If your data represents a sample of the population, compute the standard deviation using STDEV. For large sample sizes, STDEV and STDEVP return approximately equal values. The standard deviation is calculated using the "biased" or "n" method using the following formula:
![]()
Syntax
STDEVP(number_list)
STDEVP_(number_list)
Parameter: number_list
A list of numbers or dataseries separated by commas.
Examples
When MEA123.ACT() has the values [1,0 2,0 3,0 4,0 5,0 6,0 7,0 8,0 9,0 10,0]:
STDEVP(MEA123.ACT(AllToDate)) returns [0,0 0,5 0,8 1,1 1,4 1,7 2,0 2,3 2,6 2,9]
STDEVP(MEA123.ACT(All)) returns [2,9 2,9 2,9 2,9 2,9 2,9 2,9 2,9 2,9 2,9]
See also
VAR
Description
Returns variance based on a sample. VAR assumes that its arguments are a sample of the population. If your data represents the entire population, then compute the variance using VARP. VAR is calculated using the following formula:
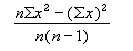
Syntax
VAR(number_list)
VAR_(number_list)
Parameter: number_list
A list of numbers or dataseries separated by commas.
Examples
When MEA123.ACT() has the values [1,0 2,0 3,0 4,0 5,0 6,0 7,0 8,0 9,0 10,0]:
VAR(MEA123.ACT(AllToDate)) returns [null 0,5 1,0 1,7 2,5 3,5 4,7 6,0 7,5 9,2]
VAR(MEA123.ACT(All)) returns [9,2 9,2 9,2 9,2 9,2 9,2 9,2 9,2 9,2 9,2]
See also
VARP
Description
Returns variance based on the entire population. VARP assumes that its arguments are the entire population. If your data represents a sample of the population, then compute the variance using VAR. VARP is calculated using the following formula:
![]()
Syntax
VARP(number_list)
VARP_(number_list)
Parameter: number_list
A list of numbers or dataseries separated by commas.
Examples
When MEA123.ACT() has the values [1,0 2,0 3,0 4,0 5,0 6,0 7,0 8,0 9,0 10,0]:
VARP(MEA123.ACT(AllToDate)) returns [0,0 0,3 0,7 1,3 2,0 2,9 4,0 5,3 6,7 8,3]
VARP(MEA123.ACT(All)) returns [8,3 8,3 8,3 8,3 8,3 8,3 8,3 8,3 8,3 8,3]
See also
Text Processing Functions
Returns a substring of S. The substring is l characters long, starting from s. |
|
Returns l leftmost characters of S. |
|
Returns l rightmost characters of S. |
|
Returns the number of characters in S. |
|
Returns S converted to lower case. |
|
Returns S converted to upper case. |
|
Replaces all occurrences of o in S by n, after which the string is returned. |
|
Returns a string which is formed by concatenating strings given as parameters. |
|
Returns the largest of the arguments. NULL is considered to be the smallest possible string. |
|
Returns the smallest of the arguments. NULL is considered to be the smallest possible string. |
|
Returns the index of the first occurrence of s in S starting from 1. If s doesn't exist in S, 0 is returned. |
|
Returns the best possible numeric interpretation of S, or 0 if S cannot be interpreted as a number at all. |
|
Returns the text given to it from which any leading and/or tailing whitespaces are removed. |
|
Returns the text given to it in reverse order. |
|
Returns the text given to it repeated n times. |
Note that all the functions listed in this section take string(s) as parameter(s). If a number is given to them as a parameter when string is expected, the number is converted to string.
MID
Description
Returns a substring of S. The substring is l characters long, starting from s.
Syntax
MID(S,s,l)
Parameter: S, String, the text to process
Parameter: s, Integer, index of the start position (starting from 1)
Parameter: l, Integer, number of characters to include
Examples
This function returns "xam":
MID("Example",2,3)
LEFT
Description
Returns l leftmost characters of S.
Syntax
LEFT(S,l)
Parameter: S, String, the text to process
Parameter: l, Integer, number of characters to include
Examples
This function returns "Exa":
LEFT("Example",3)
RIGHT
Description
Returns l rightmost characters of S.
Syntax
RIGHT(S,l)
Parameter: S, String, the text to process
Parameter: l, Integer, number of characters to include
Examples
This function returns "ple":
RIGHT("Example",3)
LENGTH
Description
Returns the number of characters in S.
Syntax
LENGTH(S)
Parameter: S, String, the text to process
Examples
This function returns 7:
LENGTH("Example")
LOWER
Description
Returns S converted to lower case.
Syntax
LOWER(S)
Parameter: S, String, the text to process
Examples
This function returns "example":
LOWER("EXAmple")
UPPER
Description
Returns S converted to upper case.
Syntax
UPPER(S)
Parameter: S, String, the text to process
Examples
This function returns "EXAMPLE":
UPPER("EXAmple")
REPLACE
Description
Replaces all occurrences of o in S by n, after which the string is returned.
Syntax
REPLACE(S,o,n)
Parameter: S, String, the text to process
Parameter: o, String, the text to search for
Parameter: n, String, the text to replace the searched string
Examples
This function returns "FooForFoz":
REPLACE("FooBarBaz","Ba","Fo")
CONCATENATE
Description
Returns a string which is formed by concatenating strings given as parameters.
Syntax
CONCATENATE(S1...n)
Parameter: S1...n, Any number of strings to be concatenated
Examples
This function returns "Example":
CONCATENATE("Ex","amp","le")
SMAX
Description
Returns the largest of the arguments. NULL is considered to be the smallest possible string.
Syntax
SMAX(S1...n)
Parameter: S1...n, Any number of strings to be compared
Examples
This function returns "FOO":
SMAX("FOO","BAR")
SMIN
Description
Returns the smallest of the arguments. NULL is considered to be the smallest possible string.
Syntax
SMIN(S1...n)
Parameter: S1...n, Any number of strings to be compared
Examples
This function returns "BAR":
SMIN("FOO","BAR")
FIND
Description
Returns the index of the first occurrence of s in S starting from 1. If s doesn't exist in S, 0 is returned.
Syntax
FIND(s,S)
Parameter: s, String, text to search for
Parameter: S, String, text to process
Examples
This function returns 2:
FIND("x","Example")
TONUMBER
Description
Returns the best possible numeric interpretation of S, or 0 if S cannot be interpreted as a number at all. While doing the conversion, leading whitespaces are removed and characters are processed until first non-numeric character is found.
Syntax
TONUMBER(S)
Parameter: S, String, the text to parse
Examples
This function returns 1012:
TONUMBER(" 10AB12")
TRIM
Description
Returns the text given to it from which any leading and/or tailing whitespaces are removed.
Syntax
TRIM(S)
Parameter: S, String, the text to trim
Examples
This function returns "Example":
TRIM(" Example ")
REVERSE
Description
Returns the text given to it in reverse order.
Syntax
REVERSE(S)
Parameter: S, String, the text reverse
Examples
This function returns "elpmaxE":
REVERSE("Example")
REPEAT
Description
Returns the text given to it repeated n times.
Syntax
REPEAT(S,n)
Parameter: S, String, the text to repeat
Parameter: n, Integer, the number of repetitions
Examples
This function returns "ExampleExample":
REPEAT("Example",2)
See Also
For details on how to define a formula for an element, go to Defining Formulas.
For examples of different kinds of formulas, go to Formula Examples.
For information about calculating the values of the functions, see Calculation.
For information about the arithmetic and logical operators, see Operators.
For information about error conditions with formulas, see Error Handling.