XML Export |

|

|

|
||
XML Export |

|

|

|

|
|
|
||
![]()
![]()
QPR Modeling Client can export a model as a set of XML files with the help of the XML Export Wizard. This wizard can be opened from the Model tab of the ribbon by clicking the Export XML button.
XML Export creates an XML document of the exported model. By default the XML format is the QPR standard XML format. However, if you wish to use a different format, you have the option to use an XSLT (eXtensible Stylesheet Language Transformation) file. XSLT, which is the sophisticated stylesheet language of XML, provides the possibility to define the format.
The following lists the main features of QPR Modeling Client XML Export:
•Definition of information for the export. QPR Modeling Client model elements and attributes are defined in XML export settings file. The export settings file can also include selection criteria i.e. criteria of the exact model element attribute values that selects the exported model elements.
•The XML settings file is a normal Windows initialization file with the extension '.pgt'. Setting files are easy to create and edit. The detailed structure of integration settings file is explained in a separate document, the QPR Developer's Guide.
•QPR Modeling Client installs predefined settings file in C:\ProgramData\QPR Software\QPR 2017\2017.1\Clients\PGIntegrationTasks folder. These predefined integration tasks are shown in export wizard's list box.
•QPR Modeling Client administrators can create their own settings files to perform a variety of different integration tasks. With the Export Wizard, the user can select and execute these tasks easily. QPR Modeling Client model element and attribute names that can be used in settings file are described in QPR Developer's Guide.
•With the Export Wizard, it is also possible to select an XSLT file to execute transformation from QPR XML format to some other XML format. These eXtensible Stylesheet Language Transformation files are powerful tools to transform QPR Modeling Client XML to, for example, UML (XMI), ebXML, XML used by project management tools, etc. More information about XSLT can be found at http://www.w3c.org.
The structure of XML export file follows the QPR XML format. The XML format is fully explained in the QPR Developer's Guide.
Note that importing a model with a changes log bigger than 1 MB is not supported. Therefore, exporting the model changes log is disabled by default.
Using the XML Export Wizard
In the first step of the XML Export Wizard, you can define which elements and attributes are exported by selecting from the different settings options. Choose whether to use an existing settings file (file type ' *.pgt ') or to use one of the predefined settings. If you select to use predefined settings, you can choose from "Export all", "Export measure data", "Export names and descriptions", and "Export resources". If you select "Export all", for example, then all elements of the model will be exported.
Once you have selected the export settings, click Next > to continue to the next step.
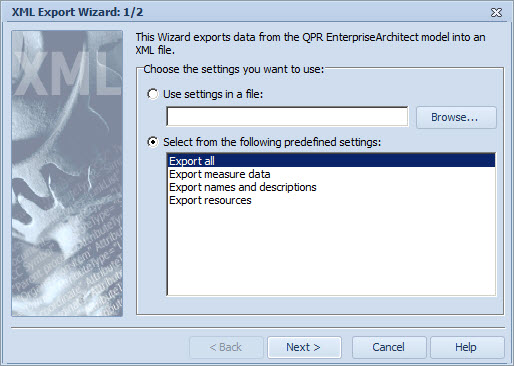
Selecting the export settings
In the second step of the XML Export Wizard, define the location and name of the XML file to which the model data will be exported. The export file can either be a new file or an already existing file. You can enter the location and name either manually or by clicking the Browse... button.
If you wish to use an XSLT file (file type ' *.xsl ') rather than the QPR standard XML format, you can define the file's location and name in the lower field. Again, you can enter the location and name either manually or by clicking the Browse... button.
Once you have completed the file definition(s) in this step, you have completed the wizard and you can click the Finish button to execute the XML export. If you wish to return to the previous step to view or modify your previous selections, click the < Back button.
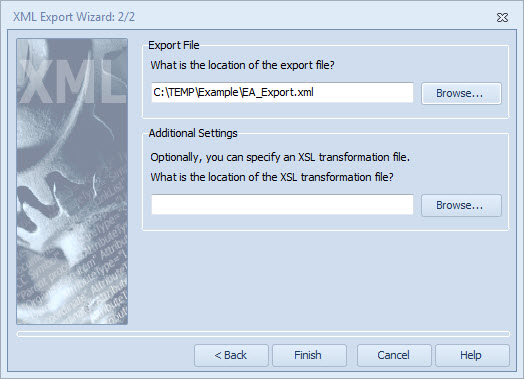
Selecting the location of the export file or the XSL transformation file
You will receive a confirmation stating whether the export was completed successfully. Once the export has been completed successfully, you can access the XML export file in the location where you have defined it to be in step 2.